The Role and Importance of a Production Software Development Center
A production software development center plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing and business operations. It serves as the hub for developing, maintaining, and optimizing software solutions that enhance productivity, ensure quality control, and streamline processes. Among its critical functions are the integration of advanced technologies, customization of software to meet specific operational needs, and continuous improvement of existing systems. This center is essential for companies looking to stay competitive in a technologically advanced market, as it provides the necessary tools and innovations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall operational performance.
I、DEFINITION AND FUNCTIONS OF A PRODUCTION SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT CENTER
A production software development center is a specialized unit within an organization that focuses on creating and managing software applications tailored for production and manufacturing processes. This center typically encompasses a team of software engineers, developers, testers, and project managers who work collaboratively to ensure that the software solutions meet the unique needs of the organization. Key functions include software design and development, system integration, maintenance and support, and process optimization.
Software Design and Development: This involves creating bespoke software solutions that address specific production requirements. Developers work on designing user-friendly interfaces, robust back-end systems, and efficient algorithms to handle complex production tasks. Custom software can range from simple applications for task scheduling to comprehensive Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems that manage all aspects of production.
System Integration: Integrating various software systems and tools is critical for seamless operations. The development center ensures that new software solutions can effectively communicate with existing systems, such as machinery, databases, and other enterprise applications. This integration helps in creating a cohesive and efficient production environment.
Maintenance and Support: Continuous maintenance and support are vital to ensure that the software remains functional and up-to-date. This includes regular updates, bug fixes, and performance enhancements. The development center also provides technical support to address any issues that may arise during the software’s lifecycle.
Process Optimization: By analyzing production data and workflows, the center identifies areas for improvement and implements software solutions to streamline processes. This could involve automating repetitive tasks, improving data accuracy, or enhancing decision-making through advanced analytics.
II、IMPORTANCE OF A PRODUCTION SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT CENTER
The significance of a production software development center cannot be overstated. It acts as the backbone of modern production facilities, enabling them to operate efficiently and effectively. Several key factors highlight its importance:
Enhancing Productivity: By automating routine tasks and optimizing workflows, the development center helps to significantly boost productivity. Software solutions can manage inventory, schedule tasks, monitor production lines, and ensure that resources are used optimally. This reduces downtime and allows for faster production cycles.
Ensuring Quality Control: Maintaining high quality standards is crucial in production. The development center develops software that monitors quality at every stage of the production process. This includes tracking metrics, generating reports, and alerting operators to any deviations from set standards. Such systems help in early detection of defects, minimizing waste and ensuring product consistency.
Reducing Costs: Efficient software solutions contribute to cost savings by optimizing resource usage, reducing waste, and minimizing downtime. Automated systems require less manual intervention, which lowers labor costs and reduces the likelihood of human error. Additionally, predictive maintenance software can foresee potential equipment failures, allowing for timely repairs and avoiding costly breakdowns.
Data-Driven Decision Making: The development center provides tools for collecting and analyzing production data. This data-driven approach enables managers to make informed decisions based on real-time information. Advanced analytics and reporting tools can identify trends, forecast demand, and optimize supply chain management, leading to better strategic planning.
Staying Competitive: In a rapidly evolving market, staying competitive requires constant innovation and improvement. The development center ensures that the organization remains at the forefront of technological advancements. By adopting the latest software solutions and integrating emerging technologies such as AI and IoT, companies can maintain a competitive edge.
III、KEY COMPONENTS OF A PRODUCTION SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT CENTER
A fully functional production software development center comprises several critical components, each playing a distinct role in the software development lifecycle. These components include the development team, infrastructure, development tools, and methodologies.
Development Team: The backbone of any software development center is its team. This includes software engineers, developers, testers, project managers, and support staff. Each team member brings specific expertise, whether in coding, system architecture, quality assurance, or project management. Collaboration and communication within the team are essential for successful software development.
Infrastructure: The physical and digital infrastructure is crucial for efficient software development. This includes hardware such as servers, workstations, and networking equipment, as well as software tools for development, testing, and deployment. A robust infrastructure ensures that the development process runs smoothly and that the software can be tested in an environment similar to the production setting.
Development Tools: Various tools and platforms are used throughout the software development lifecycle. These include Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), version control systems, testing frameworks, and deployment automation tools. Utilizing the right tools enhances productivity, improves code quality, and facilitates collaboration among team members.
Methodologies: Adopting appropriate development methodologies is critical for organizing and managing the development process. Agile, DevOps, and Lean are popular methodologies that emphasize iterative development, continuous integration, and rapid delivery. These methodologies promote flexibility, improve collaboration, and ensure that the software meets the evolving needs of the production environment.
IV、CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS IN PRODUCTION SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
Despite its importance, production software development is not without challenges. Common issues include managing complexity, ensuring security, maintaining compatibility, and handling scalability.
Managing Complexity: Production environments are inherently complex, with numerous interdependent systems and processes. Developing software that can handle this complexity requires thorough planning, detailed requirements gathering, and comprehensive testing. Solutions include modular design, where the software is broken down into smaller, manageable components, and the use of simulation tools to model and test different scenarios.
Ensuring Security: Security is a major concern in production software development, given the potential for cyber-attacks and data breaches. Ensuring robust security involves implementing best practices such as encryption, access control, and regular security audits. Additionally, staying updated with the latest security threats and vulnerabilities helps in proactively addressing potential risks.
Maintaining Compatibility: Production environments often involve a mix of legacy systems and modern technologies. Ensuring that new software solutions are compatible with existing systems is crucial to avoid disruptions. This requires thorough testing, use of standard protocols, and, when necessary, developing custom integration solutions to bridge any gaps.
Handling Scalability: As production demands grow, the software must be capable of scaling accordingly. This involves designing the software architecture to support additional users, increased data volume, and higher transaction rates. Cloud-based solutions and scalable infrastructure can help address scalability challenges by providing the necessary resources on-demand.
V、FUTURE TRENDS IN PRODUCTION SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
The field of production software development is continually evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing industry needs. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of this domain, including the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Industry 4.0 principles.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming production software by enabling more sophisticated data analysis, predictive maintenance, and automation. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of production data to identify patterns, optimize processes, and predict potential issues before they occur. AI-driven automation further enhances efficiency by handling repetitive tasks and making real-time adjustments to production parameters.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT technology connects various devices and sensors within the production environment, creating a network of interconnected systems. This connectivity allows for real-time monitoring, data collection, and control of production processes. IoT-enabled software solutions provide valuable insights into machine performance, energy consumption, and overall operational efficiency, facilitating proactive decision-making.
Industry 4.0: The principles of Industry 4.0 emphasize the integration of digital technologies into production processes. This includes the use of cyber-physical systems, advanced robotics, and digital twins. Production software development centers play a key role in implementing these technologies, creating intelligent and interconnected production systems that are more adaptable, efficient, and responsive to market demands.
Cloud Computing: Cloud-based solutions offer significant advantages in terms of scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. By leveraging cloud infrastructure, production software can be rapidly deployed, updated, and scaled to meet changing needs. Additionally, cloud-based platforms facilitate collaboration among geographically dispersed teams and provide access to powerful computing resources.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to manage production data and transactions. Its decentralized nature ensures data integrity and reduces the risk of tampering. In production environments, blockchain can be used for supply chain management, tracking the provenance of materials, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
VI、CASE STUDIES: SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF PRODUCTION SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT CENTERS
Examining real-world examples of successful implementation can provide valuable insights into the benefits and best practices of production software development centers. Here are a few case studies that highlight the impact of such centers on organizational performance.
Case Study 1: Automotive Manufacturing Company: An automotive manufacturer established a production software development center to enhance its production line efficiency. By developing custom software for real-time monitoring and control of assembly lines, the company reduced downtime by 20% and improved overall production speed. The software also integrated with existing ERP systems, providing a unified platform for managing inventory, scheduling, and quality control.
Case Study 2: Electronics Manufacturer: A leading electronics manufacturer faced challenges with quality control and defect detection. The production software development center developed an AI-powered visual inspection system that used machine learning algorithms to identify defects in real-time. This system significantly reduced the rate of defective products, improved customer satisfaction, and lowered costs associated with product recalls and rework.
Case Study 3: Food and Beverage Company: A food and beverage company implemented a production software development center to optimize its supply chain and production processes. By developing an IoT-enabled software solution, the company achieved real-time monitoring of production equipment, streamlined inventory management, and enhanced traceability of raw materials. This led to a 15% reduction in operational costs and improved product quality.
Case Study 4: Pharmaceutical Company: A pharmaceutical company needed to ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards while maintaining high production efficiency. The production software development center developed a comprehensive compliance management system that automated documentation, monitoring, and reporting processes. This system not only ensured regulatory compliance but also improved production efficiency by minimizing manual intervention and reducing errors.
VII、BEST PRACTICES FOR ESTABLISHING A PRODUCTION SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT CENTER
To successfully establish and operate a production software development center, organizations should follow several best practices. These practices ensure that the center operates efficiently and delivers high-quality software solutions that meet organizational needs.
Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives of the development center. This includes identifying specific production challenges, outlining desired outcomes, and setting measurable targets. Having a clear vision helps in aligning the efforts of the development team with organizational priorities.
Invest in Talent: Building a skilled and experienced development team is crucial. Invest in recruiting top talent, providing ongoing training, and fostering a collaborative work environment. Encourage innovation and continuous learning to keep the team updated with the latest industry trends and technologies.
Adopt Agile Methodologies: Agile methodologies promote iterative development, continuous feedback, and rapid delivery. Implementing agile practices helps in responding to changing requirements, improving collaboration, and delivering software solutions more efficiently. Regular sprints, daily stand-ups, and retrospective meetings are key components of agile methodologies.
Leverage Technology: Utilize advanced development tools and technologies to enhance productivity and improve software quality. This includes version control systems, automated testing frameworks, and cloud-based development platforms. Leveraging technology helps in streamlining the development process and ensuring that the software meets high standards.
Prioritize Security: Security should be a top priority in production software development. Implement best practices such as secure coding standards, regular security audits, and encryption of sensitive data. Stay updated with the latest security threats and vulnerabilities to proactively address potential risks.
Focus on User Experience: Developing user-friendly software is essential for ensuring high adoption rates and user satisfaction. Involve end-users in the development process to gather feedback and understand their needs. Conduct usability testing to identify and address any issues that may impact the user experience.
Measure and Improve: Continuously measure the performance of the development center and identify areas for improvement. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress, assess the impact of software solutions, and make data-driven decisions. Regularly review and refine development processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
VIII、CONCLUSION
A production software development center is a vital asset for modern manufacturing and business operations. It enables organizations to develop, maintain, and optimize software solutions that enhance productivity, ensure quality control, and streamline processes. By adopting best practices, leveraging advanced technologies, and focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can establish a successful development center that drives innovation and maintains a competitive edge in the market. With the right approach, a production software development center can significantly contribute to the overall success and growth of an organization.
相关问答FAQs:
1. What is a Software Development Center (SDC)?
A Software Development Center (SDC) is a dedicated facility or team within an organization that focuses on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software applications. It serves as the hub for all software development activities and typically houses a team of software engineers, developers, testers, project managers, and other professionals involved in the software development process.
2. What are the key functions of a Software Development Center?
The key functions of a Software Development Center include:
- Requirement Analysis: Understanding the client's needs and translating them into software requirements.
- Design and Architecture: Planning the structure and components of the software application.
- Development: Writing code and building the software based on the design and requirements.
- Testing: Conducting various tests to ensure the software functions correctly and meets quality standards.
- Deployment: Installing the software in the production environment for end-users to use.
- Maintenance: Providing ongoing support, updates, and bug fixes for the software.
3. What are the benefits of establishing a Software Development Center?
Establishing a Software Development Center offers several benefits, including:
- Cost Efficiency: Centralizing software development activities can lead to cost savings through economies of scale and resource optimization.
- Quality Control: Having a dedicated team focused on software development ensures better quality control and adherence to standards.
- Knowledge Retention: By centralizing expertise and knowledge within the center, organizations can better retain and leverage intellectual capital.
- Collaboration: Co-locating software development teams fosters collaboration, communication, and knowledge sharing among team members.
- Scalability: SDCs can easily scale their operations up or down based on project requirements, ensuring flexibility and adaptability.
In conclusion, a Software Development Center plays a crucial role in the software development lifecycle, offering a centralized hub for all development activities and enabling organizations to efficiently design, build, test, and maintain software applications.

 阅读时间:6 分钟
阅读时间:6 分钟  浏览量:3833次
浏览量:3833次


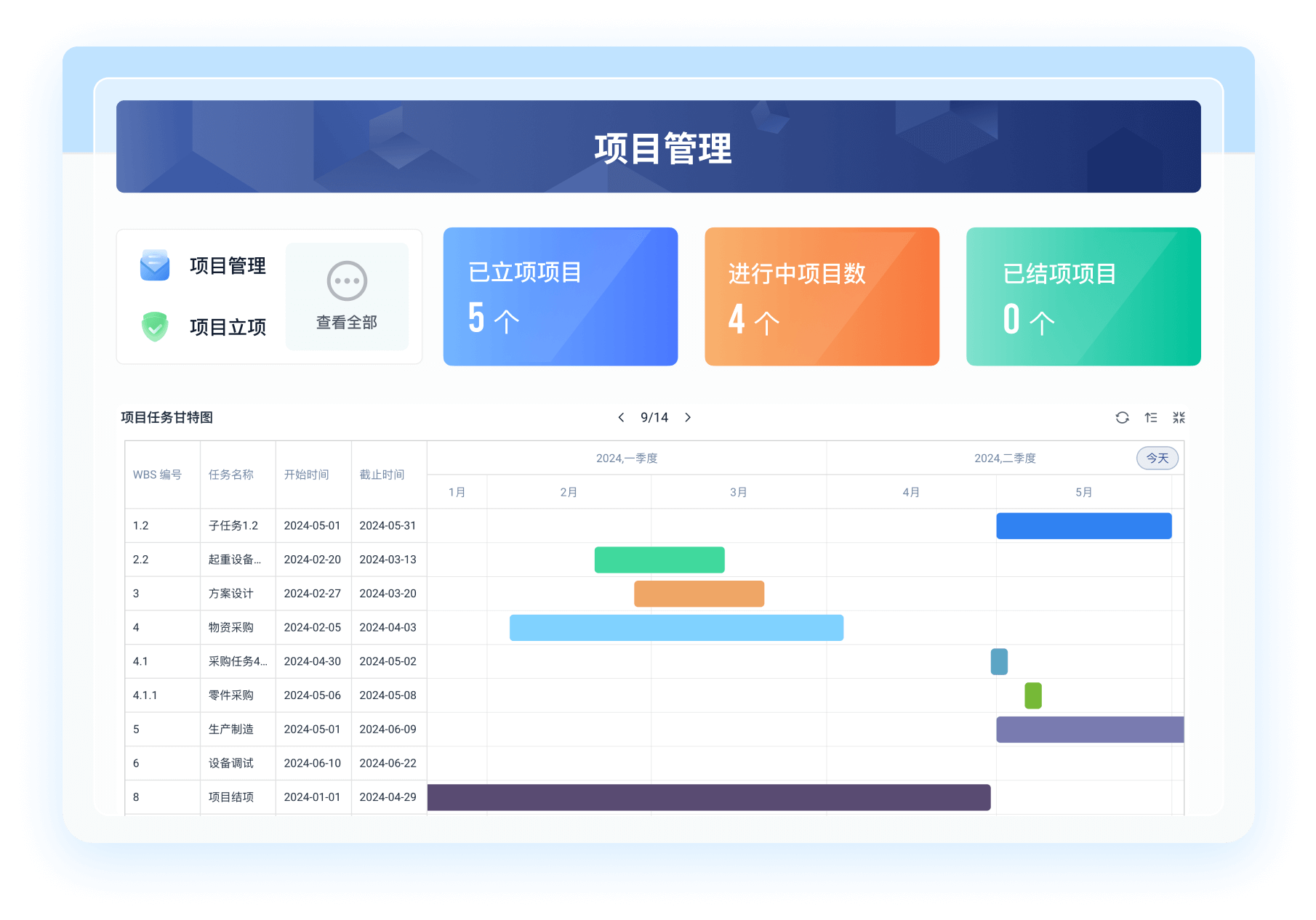
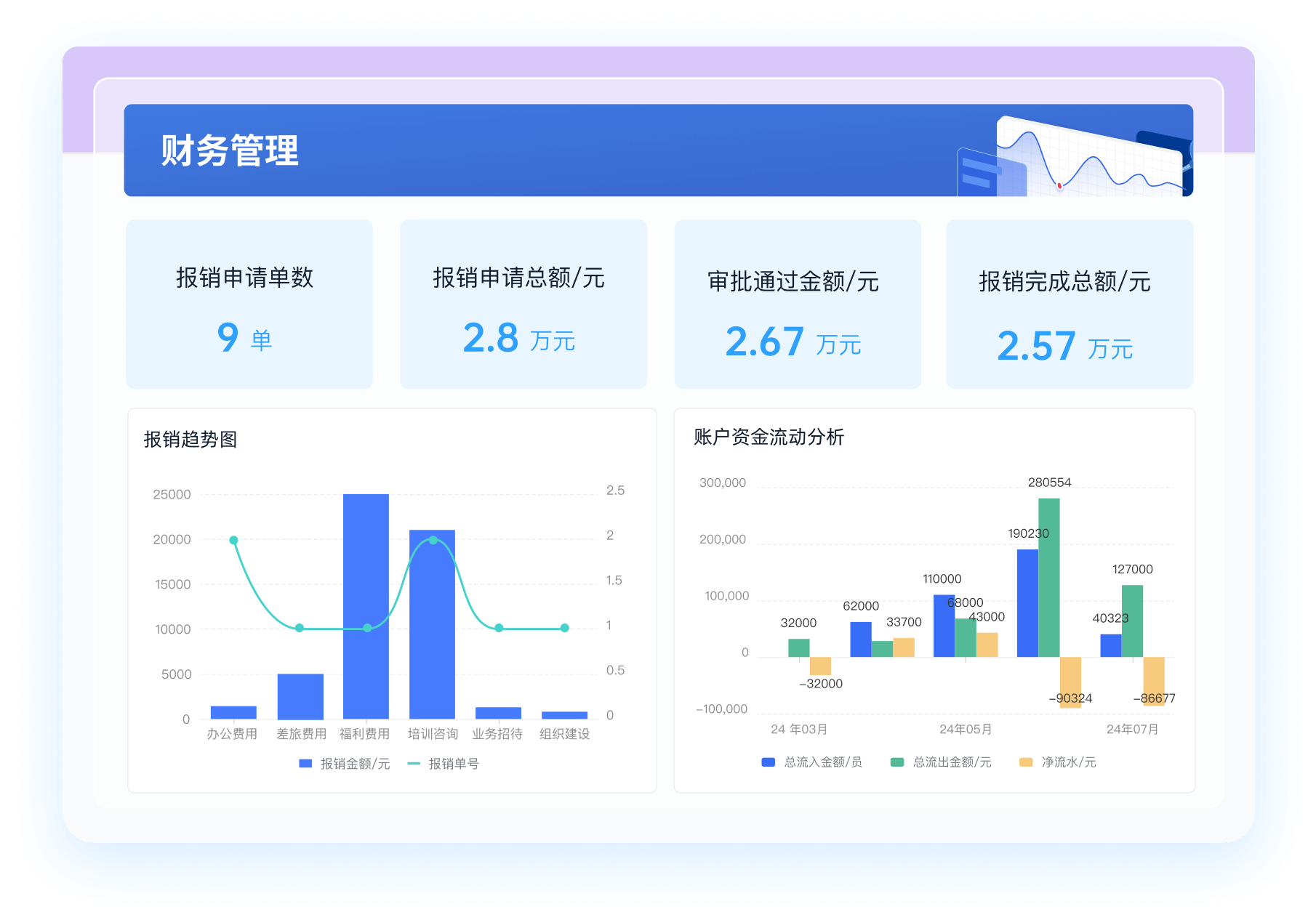



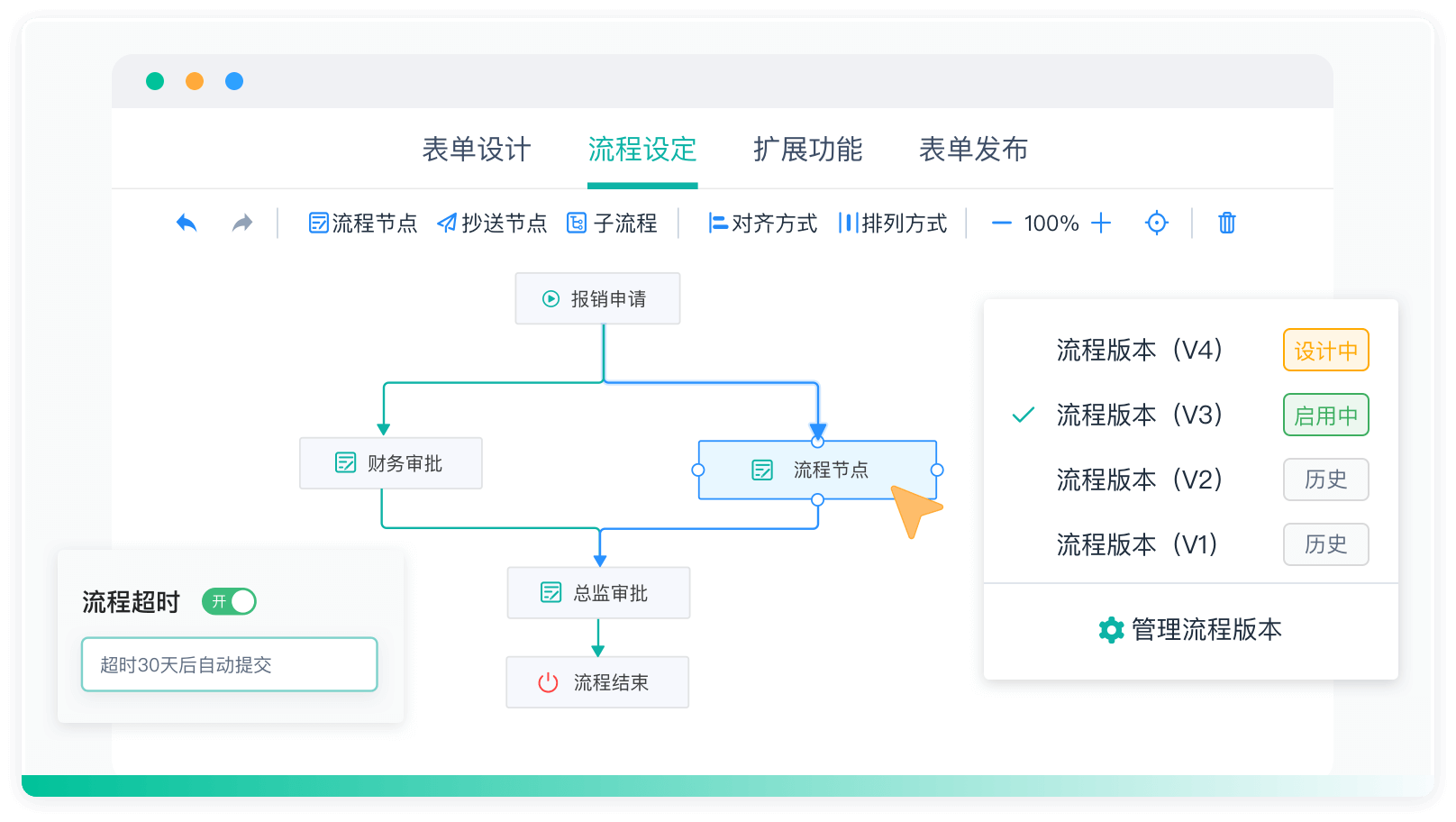
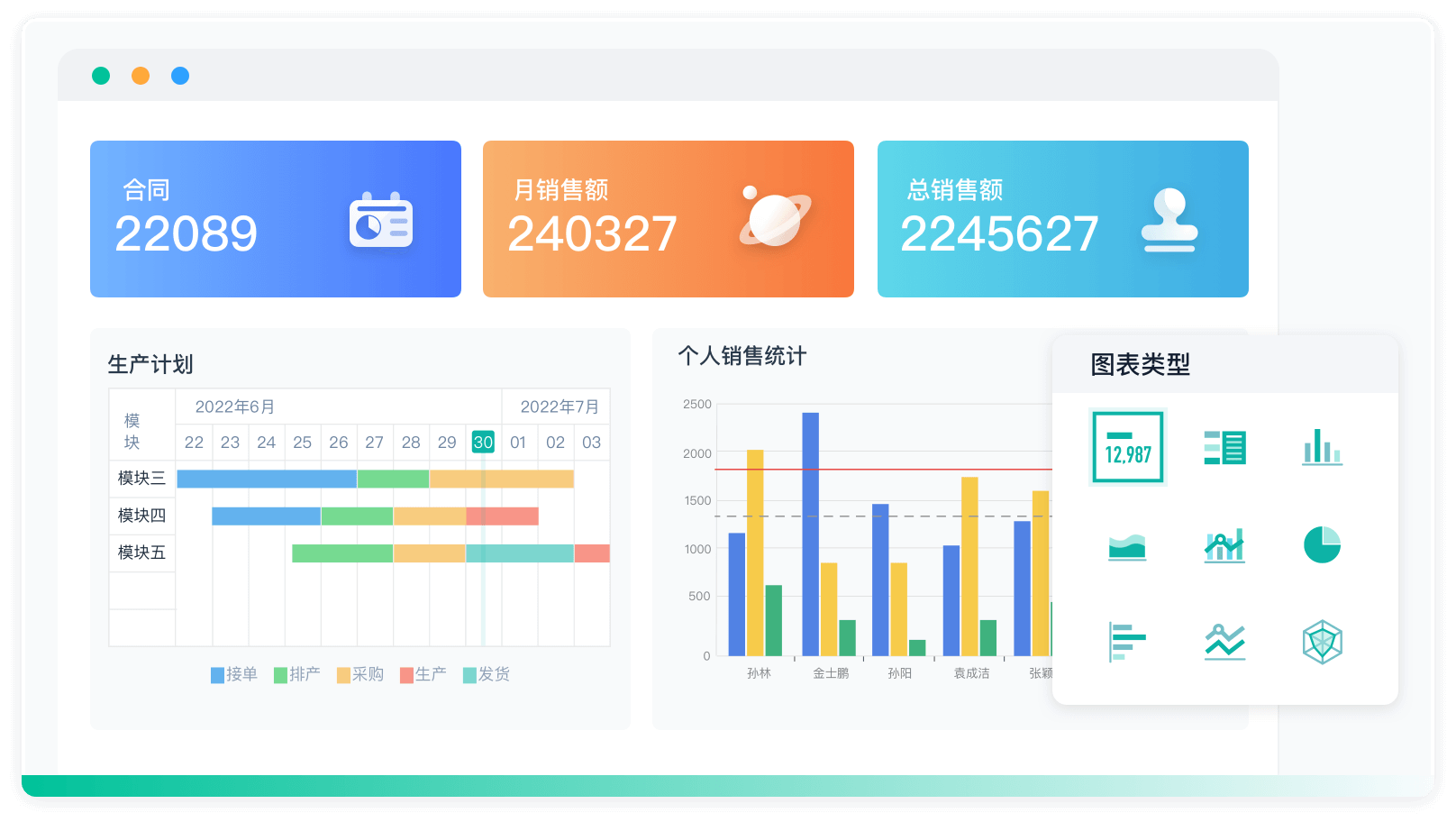
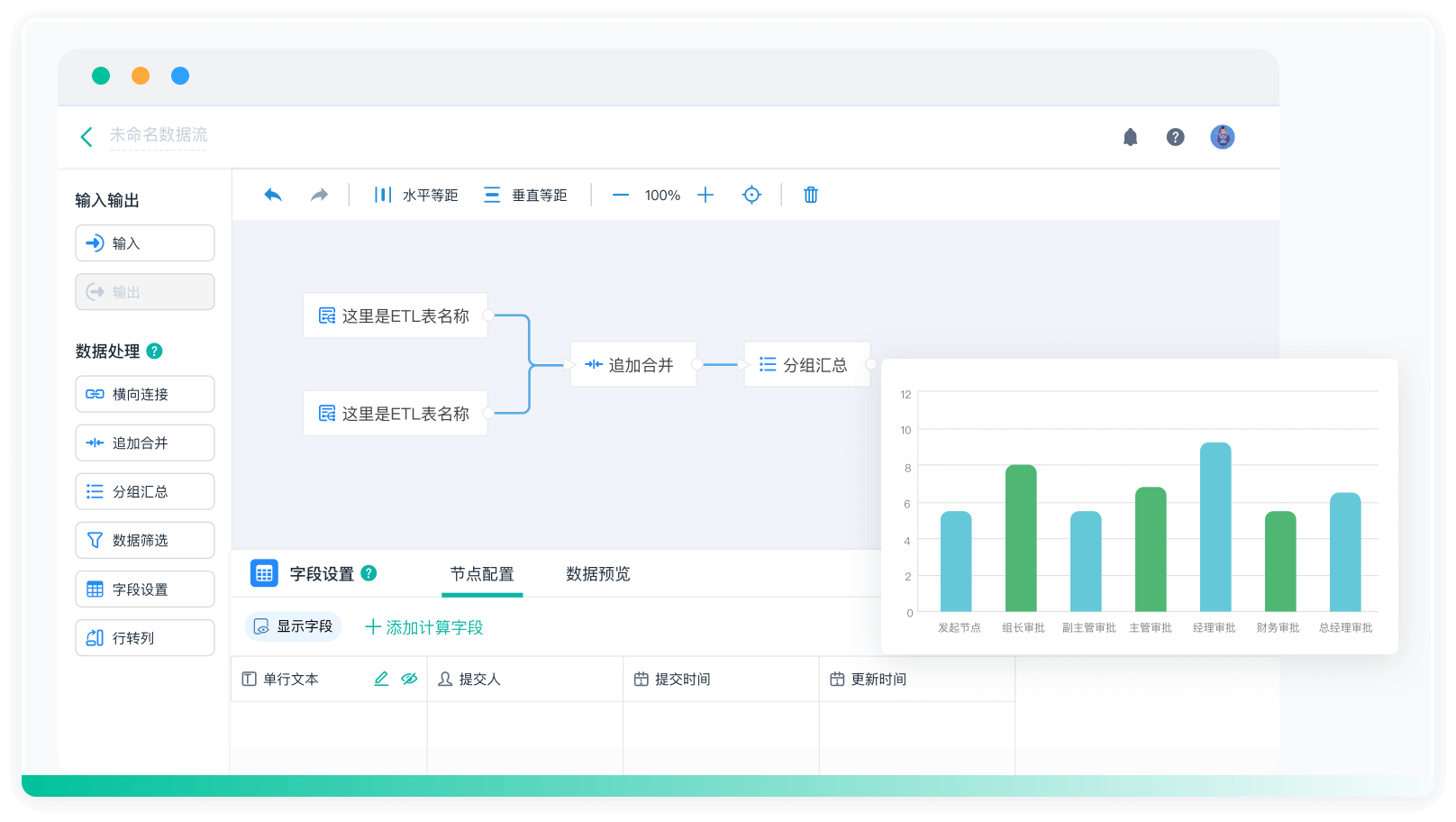
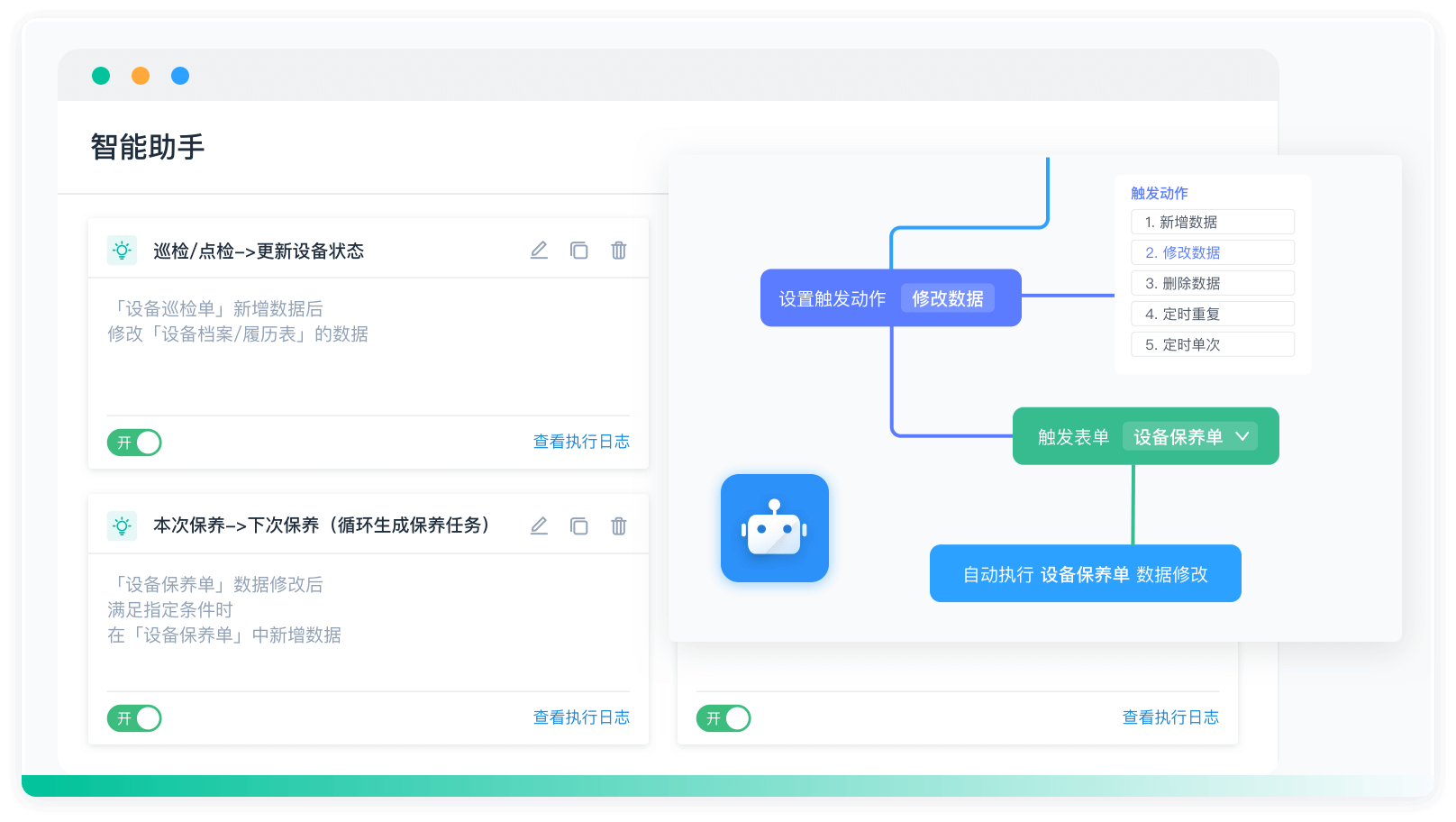





























































 《零代码开发知识图谱》
《零代码开发知识图谱》
 《零代码
新动能》案例集
《零代码
新动能》案例集
 《企业零代码系统搭建指南》
《企业零代码系统搭建指南》









